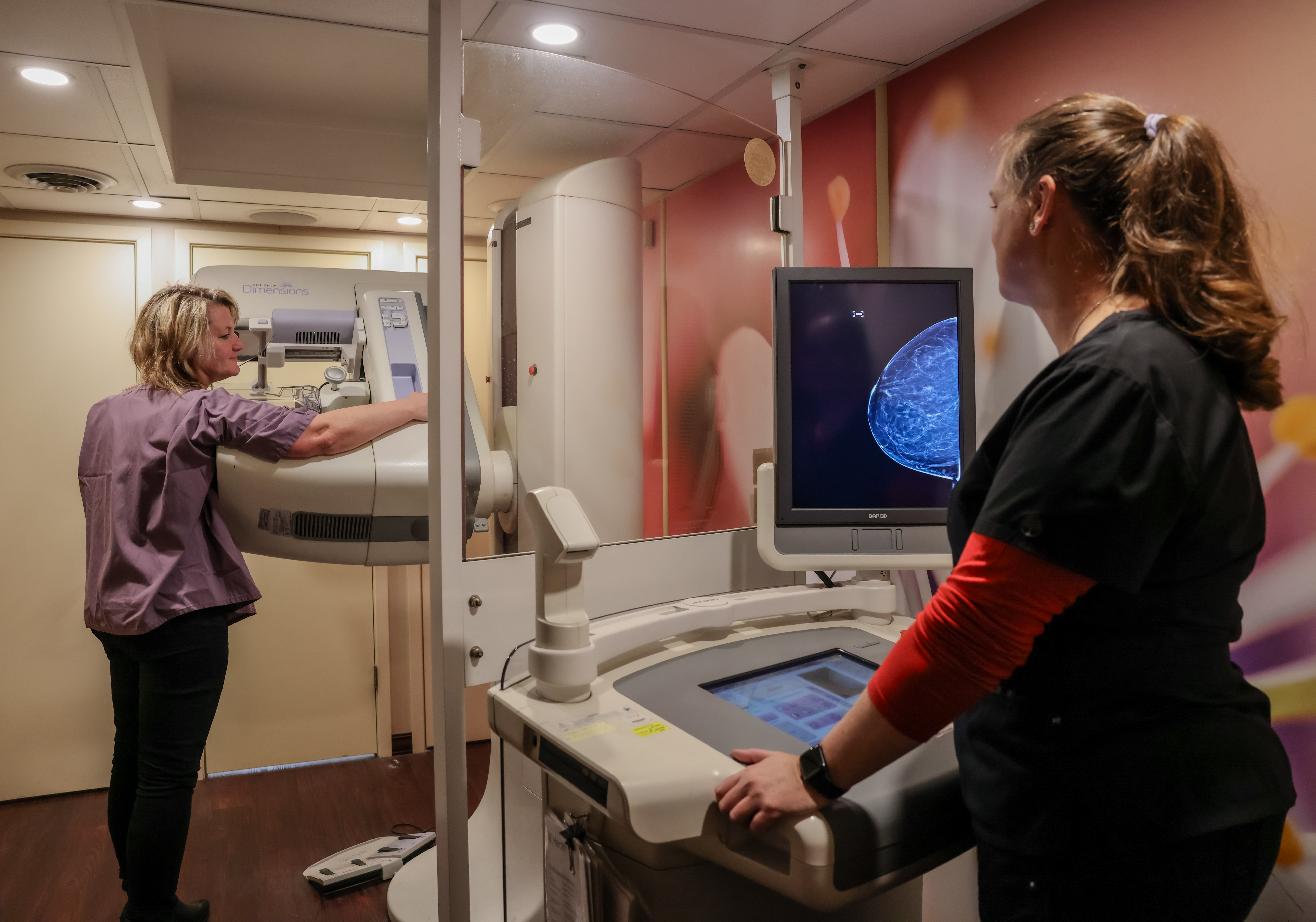
Early detection is crucial in the fight against cancer. By leveraging advanced diagnostic technologies, we offer comprehensive screenings designed to identify cancer at its earliest, most treatable stages. Our experienced healthcare professionals ensure that each individual receives personalized care tailored to their unique needs. Regular screening can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment, offering peace of mind and empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to take proactive steps toward their health.
To schedule an appointment, please call the Cancer Screening team at 513-475-8000.